What is AS9120 Risk Management?
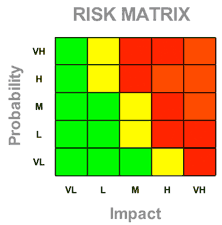 Risks have future consequences, and can be “closed” only after successful mitigation through avoiding, controlling, transferring, or assuming the risk. Each risk event has three components:
Risks have future consequences, and can be “closed” only after successful mitigation through avoiding, controlling, transferring, or assuming the risk. Each risk event has three components:
- A future root cause
- The probability of the future root cause occurring
- The consequence/impact if the root cause occurs
Buy a copy of the ARP 9134 Risk Guidance Standard
Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) can be applied proactively for the protection of all procured products and services (flying and non-flying) through all levels of the supply chain. The guideline focuses on Quality as a key risk assessment factor taking into account elements from all aspects of the business having a direct link to global quality management.
AS9120 Rev B, Section 7.1.2 Risk Management says the organization shall establish, implement and maintain a process for managing risk to the achievement of applicable requirements, that includes as appropriate to the organization and the product:
- assignment of responsibilities for risk management
- definition of risk criteria (e.g., likelihood, consequences, risk acceptance)
- identification, assessment and communication of risks throughout product realization, identification, implementation and management of actions to mitigate risks that exceed the defined risk
- acceptance criteria
- acceptance of risks remaining after implementation of mitigating actions.
The IAQG Provides several helpful items:
Typical Risk Management Definitions (source: Department of Defense Risk Management Guide)
- Consequence: The outcome of a future occurrence expressed qualitatively or quantitatively, being a loss, injury, disadvantage or gain.
- Future Root Cause: The reason, which, if eliminated or corrected, would prevent a potential consequence from occurring. It is the most basic reason for the presence of a risk.
- Issue: A problem or consequence which has occurred due to the realization of a root cause. A current issue was likely a risk in the past that was ignored or not successfully mitigated.
- Risk: A measure of future uncertainties in achieving program performance goals within defined cost and schedule constraints. It has three components:
- a future root cause
- a likelihood assessed at the present time of that future root cause occurring
- the consequence of that future occurrence.
- Risk Analysis: The activity of examining each identified risk to:
- refine the description of the risk
- isolate the cause
- determine the effects
- aiding in setting risk mitigation priorities.
- It refines each risk in terms of:
- its likelihood
- consequence
- relationship to other risk areas or processes.
- Risk Identification: The activity that examines each element of the program to:
- identify associated future root causes
- begin their documentation
- set the stage for their successful management.
- Risk identification begins as early as possible in successful programs and continues throughout the life of the program.
- Risk Management: An overarching process that encompasses:
- identification
- analysis
- mitigation
- planning
- mitigation plan implementation
- tracking of future root causes and their consequence.
- Risk Management Planning: The activity of:
- developing and documenting an organized, comprehensive, and interactive strategy and methods for identifying and tracking future root causes
- developing risk-mitigation plans
- performing continuous risk assessments to determine how risks and their root causes have changed
- assigning adequate resources.
- Risk Mitigation Plan Implementation: The activity of executing the risk mitigation plan to ensure successful risk mitigation occurs.
- Determines what planning, budget, and requirements/contractual changes are needed
- provides a coordination vehicle with management and other stakeholders
- directs the teams to execute the defined and approved risk mitigation plans
- outlines the risk reporting requirements for on-going monitoring
- documents the change history.
- Risk Mitigation Planning: The activity that identifies, evaluates, and selectsoptions to set risk at acceptable levels given program constraints and objectives. It includes the specifics of:
- what should be done
- when it should be accomplished
- who is responsible
- the funding required to implement the risk mitigation plan.
- Risk Tracking: The activity of systematically tracking and evaluating the performance of risk mitigation actions against established metrics throughout the acquisition process and develops further risk mitigation options or executes risk mitigation plans, as appropriate.
- It needs information back into the other risk management activities:
- identification
- analysis
- mitigation planning
- mitigation plan implementation
Other Risk Management Resources:
- Products:
- Root Cause Analysis Training
- Procedure: MP-722 Risk Management
- Risk Management Excercise
- Download (FREE) Department of Defense Risk Management Guide
- Buy a copy of ARP 9134 Risk Guidance Standard
- IAQG Supply Chain Management Handbook (SCMH) guidance
- Read these articles:
- Quality Digest AS9120 Risk Article
- Quality Progress Article “Risk management concept expanded“


